Proxmox VE - Fedora CoreOS : Un mariage presque parfait / An almost perfect Union
Proxmox VE
Within Geco-iT, we strongly rely on Proxmox VE as an hypervisor OS since the beginning of the project (Version 0.9 - 2008). As a reminder, Proxmox VE is a free / opensource virtualization solution based on Linux QEMU/KVM :
Proxmox VE features list contains :
- Full Operating System based on latest Debian stable 64 bits
- Web GUI and CLI for Administration and Supervision
- Save and Restore tools
- Clustering functionality
- Full Virtual machine support thanks to KVM
- Linux container support thanks to LXC
- Storage management for VMs: LVM-Thin, ZFS, CEPH, iSCSI…
- Provisionning tools : Cloud-Init
Fedora CoreOS
For our Docker Swarm / Kubernetes container ochestration projects, we migrated from CoreOS distribution to Fedora CoreOS distribution.
Fedora CoreOS is an Operating system that is auto-updated, minimal and containers oriented. It is derived from Fedora Community distribution and especially designed for containerized environnement. The main goal is to support containerized workloads in a secure way.
The Fedora CoreOS distribution succeed to two projects, Fedora Atomic Host and CoreOS Container Linux. The idea is to merge, within a minimal operating system, OCI support and Atomic Host packaging with provisionning tools and automated roll-out of CoreOS.
Fedora CoreOS is the base of Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS).
Fedora CoreOS features list contains :
- Automated update with stagged roll-out
- Base System : Last Fedora
- Last stable Linux Kernel
- Provisionning tools : Ignition
- OCI Support for Docker containers by Podman and Moby
- Hardenning by SeLinux
- Out of the box Cgroups support
Intégration of VM Fedora CoreOS within Proxmox VE
Proxmox VE use Cloud-Init as a provisionning tool for Virtual Machines (VM) Cloud-Init but Fedora CoreOS is only compatible with “Ignition”. So we made a « wrapper » that convert the Cloud-Init config of proxmox to an Ignition compatible config…
Our Cloud-Init ⇔ Ignition wrapper takes care of the following parameters :
- Username ; by default = admin
- Password
- DNS Domain
- DNS server(s)
- SSH Key(s)
- IP configuration(s) but only IPv4
Source code can be seen here: https://git.geco-it.net/GECO-IT-PUBLIC/fedora-coreos-proxmox
Our tool will automatically :
- Download the Fedora CoreOS Image
- Create a virtual Machine
- Import the Fedora CoreOS as a VM Disk
- Add a cloud init config drive to that VM
- Add the « hook-script » hook-fcos.sh at VM startup
- Copy the Ignition template in a « Proxmox snippet » storage
- Convert the VM to a Template
Prerequisites
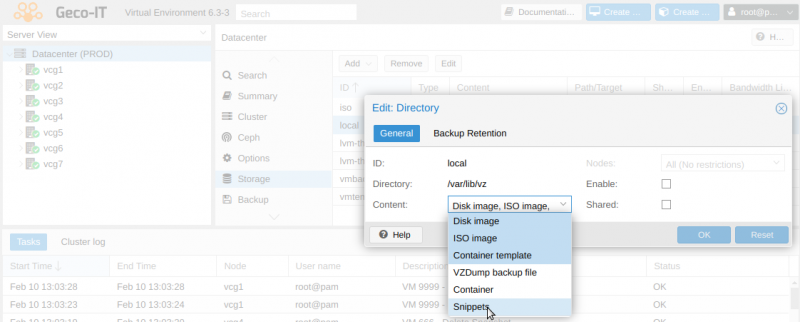
- Activate a « Proxmox snippet » storage
On the Proxmox WebUI : DATACENTER ⇒ STORAGE ⇒ Select the storage ⇒ Edit ⇒ Content ⇒ Select « Snippets »
- Download of sources files
You can visit https://git.geco-it.net/GECO-IT-PUBLIC/fedora-coreos-proxmox and download sources or use the git command in a terminal
On a linux bash shell as root :
# git install root@vcg1:~# apt install git # downloading sources files root@vcg1:~# git clone https://git.geco-it.net/GECO-IT-PUBLIC/fedora-coreos-proxmox.git ... root@vcg1:~# cd fedora-coreos-proxmox
Configuration
Configuration parameters can be found that the begining of the file vmsetup.sh. Use your text editor like vi to edit the file.
root@vcg1:~/fedora-coreos-proxmox# vi vmsetup.sh
Required config values :
- TEMPLATE_VMID=“1000”
ID that will be used as the VMID of the Fedora CoreOS template
- TEMPLATE_VMSTORAGE=“local”
Name of the proxmox storage that will be used to store the VM Template disk
- SNIPPET_STORAGE=“local”
Name of the proxmox storage for the snippet
Fedora CoreOS VM Template Creation
Once the config is saved, you can create the Fedora CoreOS VM template by launching the « vmsetup.sh » command
root@vcg1:~/fedora-coreos-proxmox# ./vmsetup.sh
Script output should look like this:
root@vcg1:~/fedora-coreos-proxmox# ./vmsetup.sh Check if vm storage thin-ssd exist... [ok] Check if snippet storage local exist... [ok] Copy hook-script and ignition config to snippet storage... 'fcos-base-tmplt.yaml' -> '/var/lib/vz/snippets/fcos-base-tmplt.yaml' 'hook-fcos.sh' -> '/var/lib/vz/snippets/hook-fcos.sh' Get storage "thin-ssd" type... [block] Download fedora coreos... fedora-coreos-32.20201018.3.0-qemu.x86_64.qcow2.xz 100%[=================>] 524.11M 59.8MB/s in 8.5s fedora-coreos-32.20201018.3.0-qemu.x86_64.qcow2.xz (1/1) 100 % 524.1 MiB / 1779.8 MiB = 0.294 55 MiB/s 0:32 Create fedora coreos vm update VM 900: -agent enabled=1 -autostart 1 -boot c -bootdisk scsi0 -cores 4 -cpu host -memory 4096 -onboot 1 -ostype l26 -tablet 0 update VM 900: -description Fedora CoreOS - Geco-iT Template - Version : 32.20201018.3.0 - Cloud-init : true Creation date : 2020-11-26 update VM 900: -net0 virtio,bridge=vmbr0 Create Cloud-init vmdisk... update VM 900: -ide2 thin-ssd:cloudinit importing disk 'fedora-coreos-32.20201018.3.0-qemu.x86_64.qcow2' to VM 900 ... transferred: 0 bytes remaining: 8589934592 bytes total: 8589934592 bytes progression: 0.00 % transferred: 91053306 bytes remaining: 8498881286 bytes total: 8589934592 bytes progression: 1.06 % transferred: 178670639 bytes remaining: 8411263953 bytes total: 8589934592 bytes progression: 2.08 % ... transferred: 8589934592 bytes remaining: 0 bytes total: 8589934592 bytes progression: 100.00 % Successfully imported disk as 'unused0:thin-ssd:vm-900-disk-0' update VM 900: -scsi0 thin-ssd:vm-900-disk-0,discard=on -scsihw virtio-scsi-pci update VM 900: -hookscript local:snippets/hook-fcos.sh Convert VM 900 in proxmox vm template... [done]
Operation diagram
- First VM boot
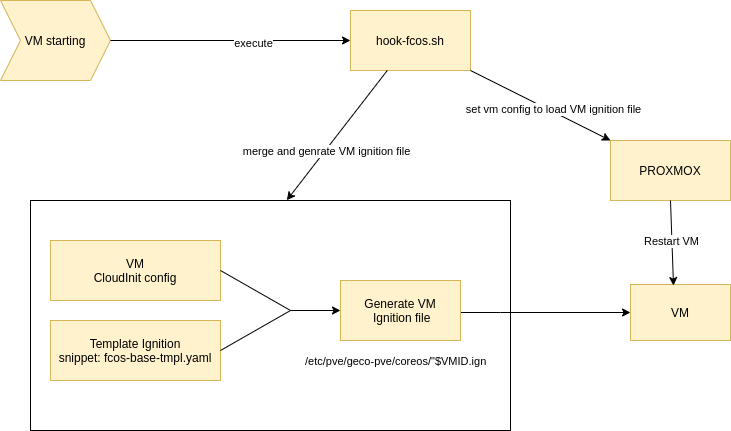
- Next VM boot
Ignition config parameters are only applied at the first VM boot.
To apply the changes made later to the Cloud-Init config, we deploy the Cloud-Init service in the VM thanks to Ignition. Cloud-Init will takes care of the future changes.
Provided Ignition Template
The« fcos-base-tmplt.yaml » ignition file that we provide is a work base. For more advanced config, please check the documentation at https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/fedora-coreos/
Our config will :
- Correct fstrim service ( Proxmox Discard Option )
- Install the Qemu-guest-agent at first boot ( network need to be operational )
- Install the Geco-iT CloudInit wrapper script ( reconfiguration if a change is detected in the Proxmox Cloud-Init config )
- Change the console log level from DEBUG (7) to WARNING (4)
- Add the Geco-iT motd/issue
Deployment of a Fedora CoreSO VM for Production use
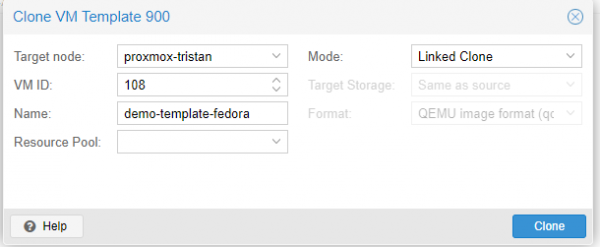
To create a Fedora CoreOS VM, the only thing to do is clone the Newly Created Fedora CoreOS template
Right click on the Fcos tmplt template ⇒ Clone ; After that you can choose cloning mode, name of the VM, etc…
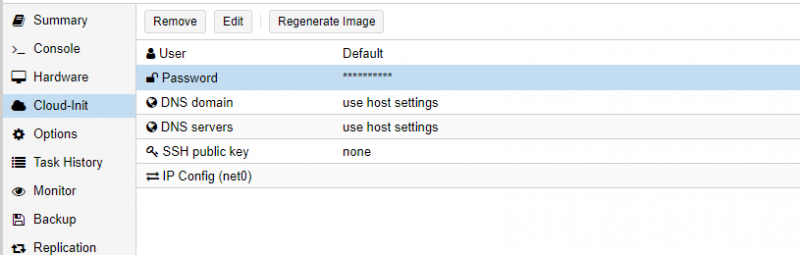
In the VM Cloud-Init menu, you must give a password and / or a ssh key to be able to login on the VM
You can start the VM
Warning ! The virtual machine will reboot automatically next to the QEMU-guest-agent, please be patient :) Reminder: default username is admin
Proxmox VE
Au sein de Geco-iT, nous utilisons en production l'hyperviseur Proxmox VE depuis les débuts du projet (Version 0.9 - 2008). Pour rappel, Proxmox VE est une solution de virtualisation libre basée sur l'hyperviseur Linux QEMU/KVM :
Proxmox VE comprend les caractéristiques suivantes :
- Système d'exploitation complet basé sur la dernière Debian Stable 64 bits
- Interface Web et CLI d'administration et de supervision.
- Outils de sauvegarde et de restauration
- Fonctions de clustering
- Support des Machines virtuelles complète grâce au module Linux KVM
- Support des containers LXC
- Gestion du stockage pour les VMs: LVM-Thin, ZFS, CEPH, iSCSI…
- Outils de provisionnement : Cloud-Init
Fedora CoreOS
Pour nos projets d’orchestration de conteneurs Docker Swarm / Kubernetes, nous avons migré de la distribution CoreOS vers la distribution Fedora CoreOS.
Fedora CoreOS est un système d’exploitation mis à jour automatiquement, minimal et orienté conteneurs. Il est dérivé de la distribution communautaire Fedora et spécialement conçue pour les environnements conteneurisés. L’objectif est de soutenir les charges de travail conteneurisées de manière sécurisée.
La distribution CoreOS entend succéder à deux autres projets, Fedora Atomic Host et de CoreOS Container Linux. L’idée est de fusionner, au sein d’un système d’exploitation minimal, le support OCI, la technologie de packaging d’Atomic Host avec les outils de provisionnement et les mises à jour automatisées de CoreOS.
Fedora CoreOS est la base de Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS).
Fedora CoreOS comprend les caractéristiques suivantes :
- Mises à jour automatiques avec déploiement par phases
- Système de base : Dernière Fedora
- Dernier Noyau Linux stable
- Outils de provisionnement : Ignition
- Support OCI et des conteneurs Docker via Podman et Moby
- Durcissement via SeLinux
- Support cgroups par défaut
Intégration de VM Fedora CoreOS dans Proxmox VE
Proxmox VE utilise comme outil de provisionnement des Machine virtuelles (VM) Cloud-Init mais Fedora CoreOS n'est compatible qu'avec Ignition. Nous avons donc écrit un outil « wrapper » qui convertit la configuration Cloud-Init de proxmox en configuration compatible Ignition.
Notre wrapper Cloud-Init ⇔ Ignition prend en compte les paramètres suivants :
- Le nom de l’utilisateur ; par défaut = admin
- Le mot de passe
- Le domaine DNS
- Le serveur DNS
- Le(s) clé(s) SSH
- La/les configuration(s) IP (IPv4 uniquement)
Les sources sont disponible à l'adresse: https://git.geco-it.net/GECO-IT-PUBLIC/fedora-coreos-proxmox
Notre outil va automatiquement :
- Télécharger l'image de Fedora CoreOS
- Créer une machine virtuelle
- Importer l'image Fedora CoreOS en disque vm
- Ajouter un disque de configuration Cloud-Init
- Ajouter le « hook-script » hook-fcos.sh au démarrage de la VM
- Copier le template Ignition dans un stockage « Proxmox snippet »
- Convertir la VM en modèle (VM Template)
Pré-requis
- Activer un stockage « Proxmox snippet »
Sur la WebUI de Proxmox : DATACENTER ⇒ STORAGE ⇒ Sélectionner le stockage ⇒ Edit ⇒ Content ⇒ Sélectionner « Snippets »

- Récupération des sources
Vous pouvez directement télécharger les sources sur https://git.geco-it.net/GECO-IT-PUBLIC/fedora-coreos-proxmox ou utiliser la commande git
En console linux root :
# installation git root@vcg1:~# apt install git # récupération des sources root@vcg1:~# git clone https://git.geco-it.net/GECO-IT-PUBLIC/fedora-coreos-proxmox.git ... root@vcg1:~# cd fedora-coreos-proxmox
Configuration
Les paramètres de configuration se trouvent en début du fichier vmsetup.sh. Utilisez votre éditeur de texte favoris (vi, joe, nano…) pour éditer ce fichier
root@vcg1:~/fedora-coreos-proxmox# vi vmsetup.sh
Paramétrage minimal :
- TEMPLATE_VMID=“1000”
L'id qui sera utilisé pour la VM Fedora CoreOS modèle
- TEMPLATE_VMSTORAGE=“local”
Le stockage Proxmox pour le disque de la VM modèle
- SNIPPET_STORAGE=“local”
Le stockage Proxmox Snippet
Création de la VM Fedora CoreOS modèle
Une fois la configuration effectuée, vous pouvez créer le modèle FCOS en lançant la commande « vmsetup.sh »
root@vcg1:~/fedora-coreos-proxmox# ./vmsetup.sh
La sortie du script devrait être:
root@vcg1:~/fedora-coreos-proxmox# ./vmsetup.sh Check if vm storage thin-ssd exist... [ok] Check if snippet storage local exist... [ok] Copy hook-script and ignition config to snippet storage... 'fcos-base-tmplt.yaml' -> '/var/lib/vz/snippets/fcos-base-tmplt.yaml' 'hook-fcos.sh' -> '/var/lib/vz/snippets/hook-fcos.sh' Get storage "thin-ssd" type... [block] Download fedora coreos... fedora-coreos-32.20201018.3.0-qemu.x86_64.qcow2.xz 100%[=================>] 524.11M 59.8MB/s in 8.5s fedora-coreos-32.20201018.3.0-qemu.x86_64.qcow2.xz (1/1) 100 % 524.1 MiB / 1779.8 MiB = 0.294 55 MiB/s 0:32 Create fedora coreos vm update VM 900: -agent enabled=1 -autostart 1 -boot c -bootdisk scsi0 -cores 4 -cpu host -memory 4096 -onboot 1 -ostype l26 -tablet 0 update VM 900: -description Fedora CoreOS - Geco-iT Template - Version : 32.20201018.3.0 - Cloud-init : true Creation date : 2020-11-26 update VM 900: -net0 virtio,bridge=vmbr0 Create Cloud-init vmdisk... update VM 900: -ide2 thin-ssd:cloudinit importing disk 'fedora-coreos-32.20201018.3.0-qemu.x86_64.qcow2' to VM 900 ... transferred: 0 bytes remaining: 8589934592 bytes total: 8589934592 bytes progression: 0.00 % transferred: 91053306 bytes remaining: 8498881286 bytes total: 8589934592 bytes progression: 1.06 % transferred: 178670639 bytes remaining: 8411263953 bytes total: 8589934592 bytes progression: 2.08 % ... transferred: 8589934592 bytes remaining: 0 bytes total: 8589934592 bytes progression: 100.00 % Successfully imported disk as 'unused0:thin-ssd:vm-900-disk-0' update VM 900: -scsi0 thin-ssd:vm-900-disk-0,discard=on -scsihw virtio-scsi-pci update VM 900: -hookscript local:snippets/hook-fcos.sh Convert VM 900 in proxmox vm template... [done]
Fonctionnement
- Premier démarrage de la VM

- Démarrage suivant
Les paramètres du fichier ignition sont seulement appliqués sur la VM lors du 1er démarrage.
Afin d'appliquer les changements de configurations Cloud-Init ultérieurs, nous déployons grâce à ignition le service Geco-CloudInit dans la VM qui s'occupera de procéder aux changements.
Modèle Ignition fournie
Le fichier ignition que nous fournissons « fcos-base-tmplt.yaml » est une base de travail. Pour une configuration avancée, veuillez-vous reporter à la documentation : https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/fedora-coreos/
Note configuration permet :
- Corrige le service fstrim (Proxmox discard option)
- Install l'agent qemu-guest-agent au 1er démarrage (le réseau doit être opérationnel)
- Install le script wrapper Geco-iT CloudInit (reconfiguration en cas de changement de configuration Cloud-Init)
- Change le niveau de journalisation des messages de la console de DEBUG (7) à WARNING (4)
- Ajout Geco-iT motd/issue
Déploiement d'une VM FCOS production
Pour créer une VM Fedora CoreOS, il vous suffit de cloner le template qu'on vient de créer.
Clic droit sur le template Fcos tmplt ⇒ Clone ; vous pouvez ensuite choisir le mode de clonage, le nom de la vm, etc…

Dans le menu Cloud-Init de la VM, vous devez renseigner au minimum un mot de passe et/ou une clé ssh pour pouvoir vous connecter à la VM

Vous pouvez démarrer la machine virtuelle
Attention, la machine virtuelle va automatiquement redémarrer suite à l'installation de l'agent QEMU ! Rappel: l'utilisateur par défaut est admin
